VEX Attribute Glossary by John Kunz
Strings
String Manipulation
String formatting In VEX is derived from C. Where each variable to be passed into the string is formatted based on a specific format in the string.
Example in Python
this_str = f"My position:{position}, and this is my age: {age}"VS VEX
string this_str = sprintf("My position: %g, and this is my age: %f",v@P,f@age)The attributes v@P and f@age as passed in as arguments and replace %g and %f respectively.
The general form of the argument is given as [flags][width][.precision][format]
Possible Flags:
-: Left justify the result
+: Prefix numbers with + if positive, also strings will be surrounded with quotes
0: Pad zeros for numeric values
Width:
Number specifying number of spaces of the value including the decimal point. I’m not fully clear how it works with floats but int i = 100 has a width of 3, and setting it any higher will add spaces to pad the front, unless 0 flag is active, then it will pad with 0s or if - flag is active, it will pad from the end. If set to * it will take the first argument as the width.
Precision:
Number specifying number of decimal points, meaning 412.1492 has a precision of 4. If set to *it will take the either the first argument or the second argument if width is also set to *.
Formats:
%g, %p, %cInteger, float, vector, vector4, matrix3, matrix, string (General)%f, %e, %EFloat, vector, vector4, matrix3, matrix (Floating Point)%sString%d, %iInteger in decimal format%x, %XInteger in hexadecimal%oInteger in octal- Use 2
%s for a literal%
Example
int i = 100;
printf("frame%04d.jpg",i);
//Output: frame0100.jpg
string str = "this is";
string str2 = "a string";
printf("%s %s",str,str2);
//Output: this is a string
float f = 24.1
printf("%.2g%%",f)
//Output: 24.10%VEX also contains built-in functions for regex searching and matching!
Vectors and Quaternions
Rotating Quaternions
A common mistake I used to make when trying to rotate quaternions is constructing a matrix and turning the matrix into a quaternion.
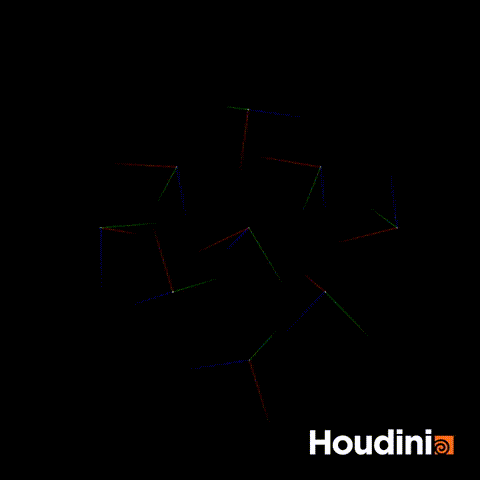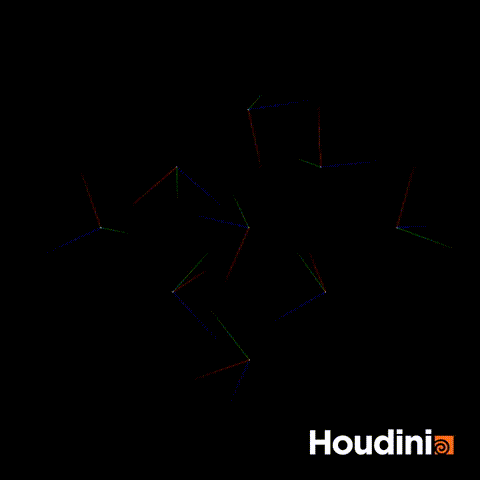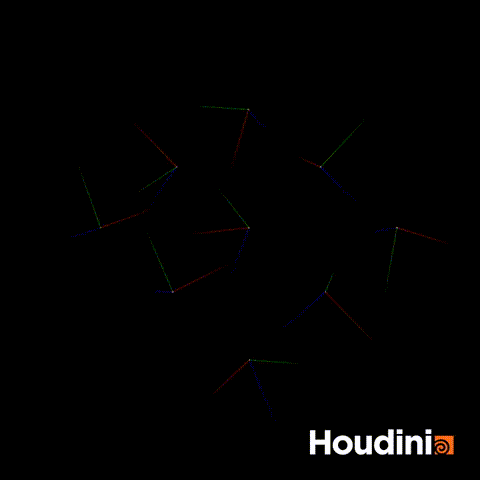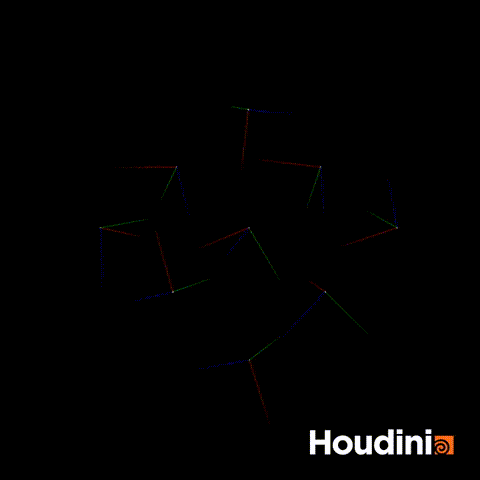
//Incorrect
matrix m = ident();
m = rotate(m,chf('angle'),{0,1,0})
vector4 rot = quaternion(m);
p@orient = qmultiply(p@orient,rot);This appears to work but you will realise that at some points, the orientation will appear to flip. This is because you are still performing the rotation step using the classic Euler rotation.
The solution is to construct the rot quaternion directly as a vector4.
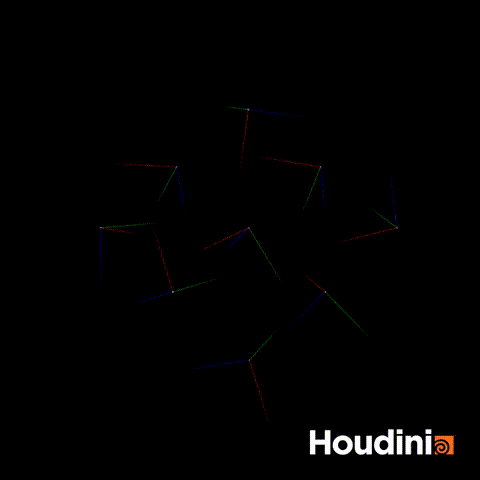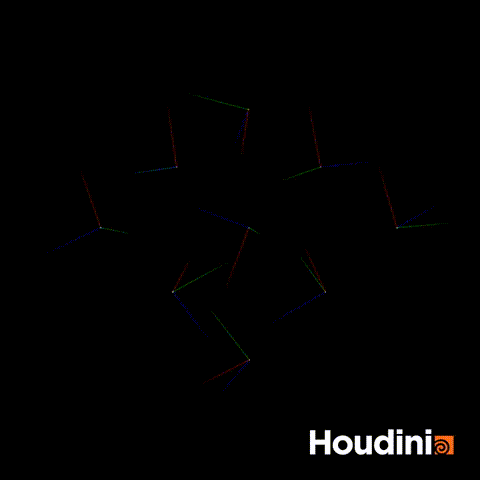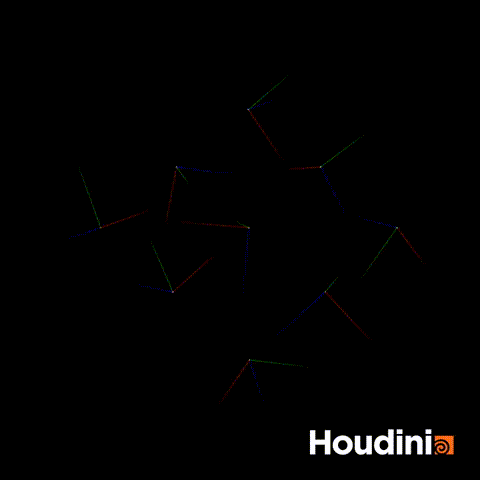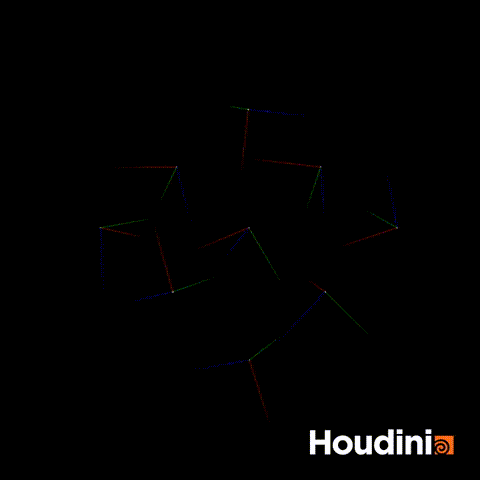
//Correct Solution
vector4 rot = quaternion(chf('angle'),{0,1,0})
p@orient = qmultiply(p@orient,rot);Now if you scrub through all values of angle, the orientation will rotate smoothly.
Getting an Axis from a Quaternion
To get the Y-Axis component from a orient:
vector y-axis = qrotate(p@orient,{0,1,0}) //Vector parameter is the AxisGetting random Vectors
If you are trying to get random vectors in VEX, your first thought might be to use vector v = rand(@ptnum) however, this has a tendency towards positive vectors and generally does not give a good result. The solution is to use built in sample functions.
Getting OBJ level transforms to VEX
The following sample code is getting a position of a camera into the wrangle.
matrix xform = optransform(ch('cam_node'));
//where cam_node can be a string or operator path parameter
vector camera_pos = xform * {0,0,0};
//in the case of a camera, the position of the point is
//exactly at 0,0,0.Instancing Alembics and modifying it’s frame offset
The current frame of an alembic primitive is stored within a intrinsic primitive attribute called ‘abcframe’.
You can pack alembics and instance it to points and you can randomize the current frame of each alembic by controlling the abcframe primintrinsic using a vex function
float seed = rand(@ptnum);
int offset = fit01(seed,0,10); //Convert 0-1 float to a int for frame values
setprimintrinsic(0, "abcframe", @ptnum, @Frame+offset);
//Set current frame of alembic to current frame + random offsetCenter UV islands
For a mesh with multiple islands, do it in a for-each connected pieces
Before
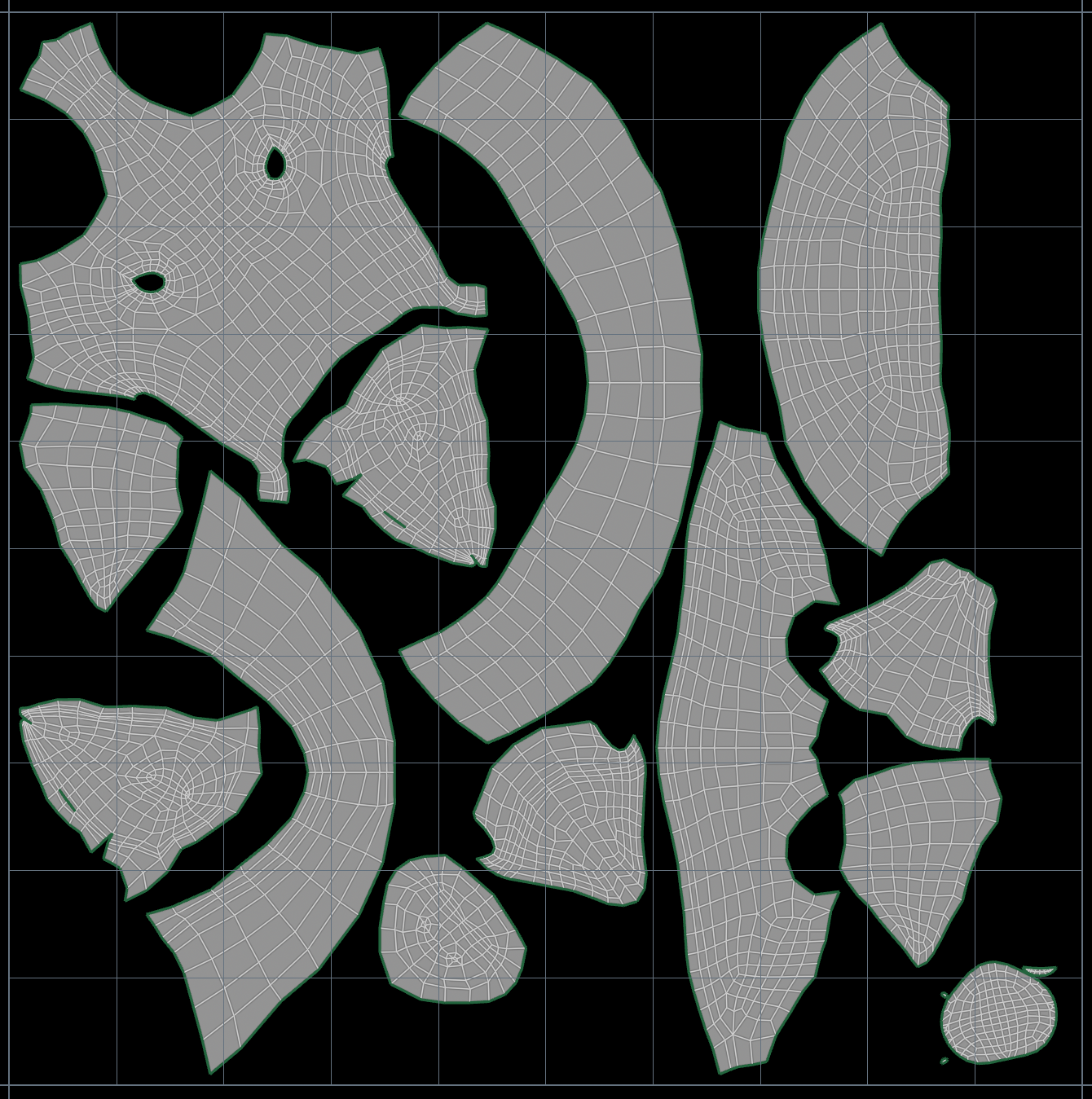

After
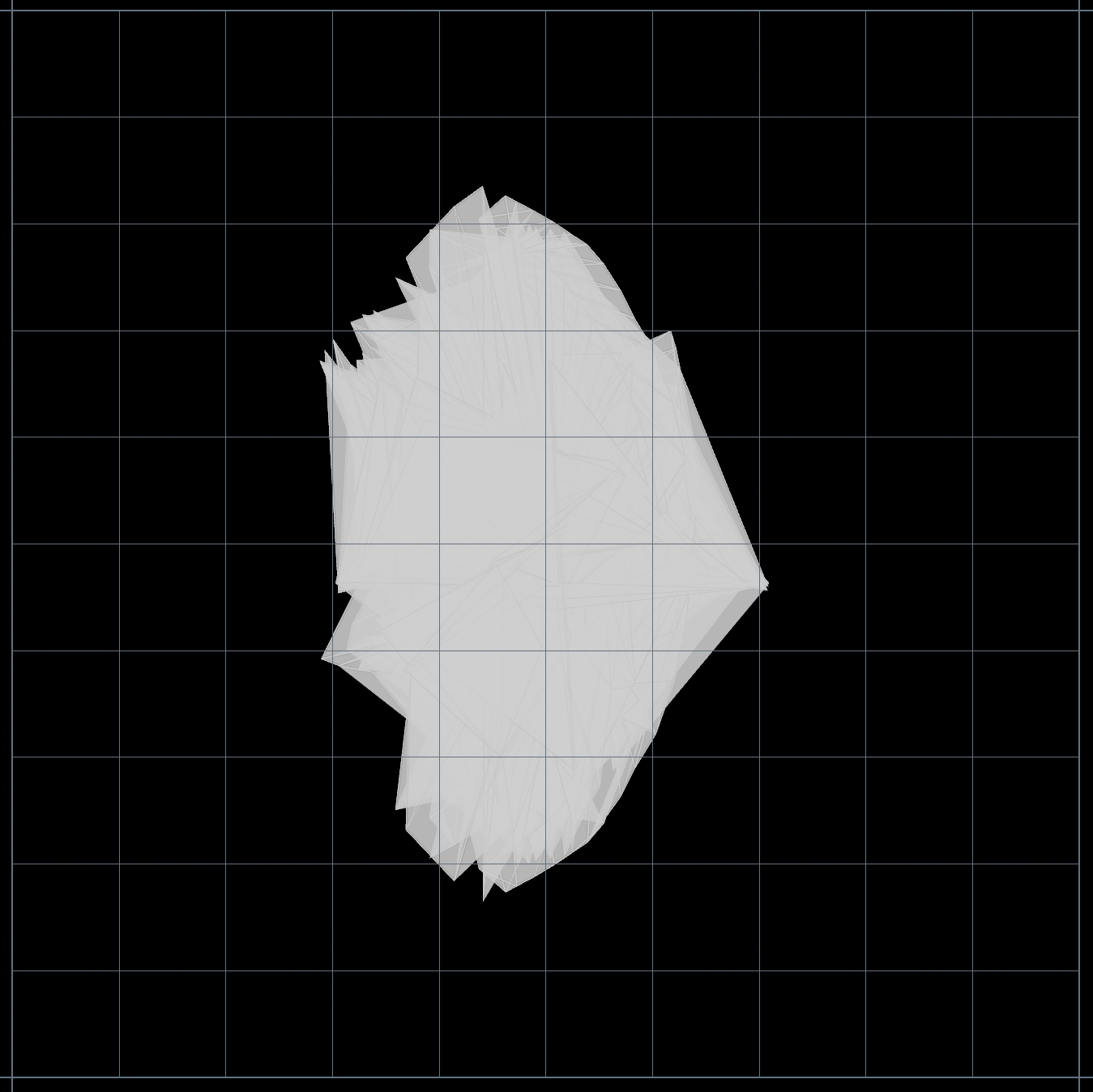

v@P = v@uv; //move point transforms to uv coords
//so that we can use built in pos functions
vector uvcenter = {0.5,0.5,0}; //bottom left is 0,0
vector bboxcenter = getbbox_center(0);
@uv +=(uvcenter - bboxcenter); //move bbox_center to uv centerGenerate Heading Vector from 2 Points / 1 Edge
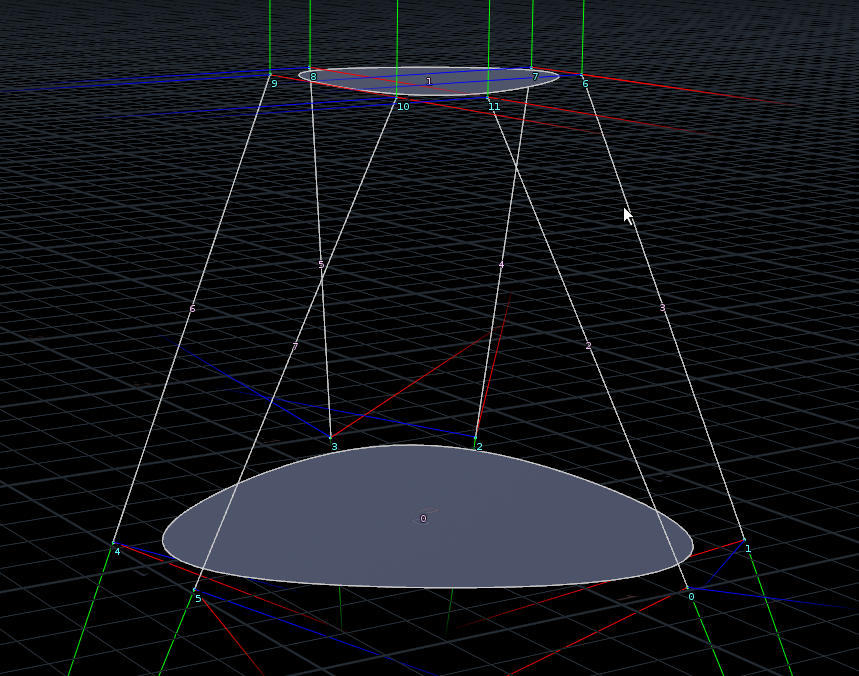
Not sure how I would describe what I was trying to accomplish, but basically I was trying to generate a heading vector that pointed in the same direction as each of these lines, while keeping the orientation of each vector to correspond to the midpoint of this whole curve.
//Get neighbouring point
int nbpt = neighbour(0,@ptnum,2);
vector nbpos = point(0,"P",nbpt);
//Generate heading vector
vector head = normalize(@P - nbpos);
vector up = {0,1,0};
//You can stop here if all you need is the heading vector
//But I wanted each of the points to have a specific orientation
v@up = cross(cross(@head,@P),@head);
//As this circle looking spline is centered at (0,0)
//@P is a vector that points towards the middle
//Using the double cross product I create a third vector
//that points outwards and is also 90 degrees to the heading vector
matrix3 xform = maketransform(-@head,@up);
p@orient = quaternion(xform);
//make transform generates a transform matrix using various params
//here I create it using two axes (green and blue axes on the screenshot)
//then I make the quaternion using the transformation matrixGenerate Oriented Bounding Boxes
The math is currently over my head but the code and explanation is here
Credits to Andy Nicholas
Oriented Bounding Boxes in VEX
A step-by-step tutorial on using VEX to calculate the oriented bounding box of geometry.
https://www.andynicholas.com/post/oriented-bounding-boxes-in-vex
Create Index by marching across a loop
Across Prims
i@index = 0;
int pPrim = 0;
int initPrim = chi('First_Prim');
for(int i = 0;i< @numprim;i++){
setprimattrib(0,'index',initPrim,i,'set');
int nb[] = polyneighbours(0,initPrim);
for(int a = 0;a<len(nb);a++){
if(nb[a]!=pPrim){
pPrim = initPrim;
initPrim = nb[a];
}
}
}Across Points
int pPoint = 0;
int ttlPoints = npoints(0);
int initPoint = chi('First_Prim');
for(int i = 0;i< ttlPoints;i++){
setpointattrib(0,'index',initPoint,i,'set');
int nb[] = neighbours(0,initPoint);
for(int a = 0;a<len(nb);a++){
if(nb[a]!=pPoint){
pPoint = initPoint;
initPoint = nb[a];
}
}
}